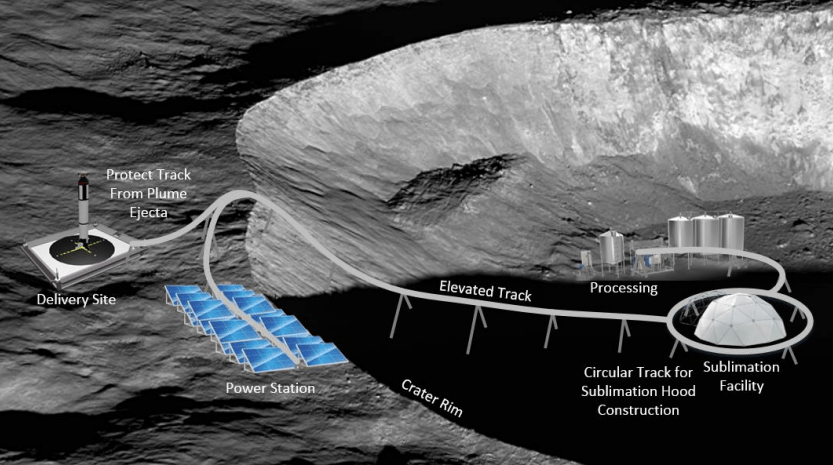
A fascinating 2019 paper explores economic feasibility of harvesting and processing lunar ice to create an affordable new source of space propellant:
https://lnkd.in/egb3W23g
Here are some of the key findings:
1️⃣ Water as a Key Resource 🌊: Water ice found in the lunar polar regions can be used not only for human consumption and radiation shielding but also for breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen. These can serve as fuel for rocket propulsion, making space exploration more sustainable by reducing the need for transporting fuel from Earth.
2️⃣ Economic Viability 💰: The study estimates that there is an annual demand for 450 metric tons of lunar-derived propellant, which equates to processing 2,450 metric tons of lunar water and generating around $2.4bn in revenue annually. The initial investment for setting up such an operation is estimated at $4bn, a relatively modest sum compared to other large-scale industrial projects.
3️⃣ Lunar Propellant Market 🚀: Refuelling spacecraft in cislunar space (the area between Earth and the Moon) using lunar-derived propellant could significantly reduce the cost of interplanetary missions, including missions to Mars. It could also enhance operations in Earth’s orbit, particularly for satellites and space stations.
4️⃣ Technological Feasibility 💡: Most of the technology required to build a lunar propellant plant already exists, requiring only adaptation for lunar conditions. This includes robotics for mining and processing, solar and nuclear power generation, and storage systems for cryogenic propellants.
5️⃣ Automation and Robotics 🤖: The entire operation, from mining lunar ice to producing and storing propellant, is envisioned to be conducted by robotic systems. Human presence is not required, which reduces risks and costs. However, the design and deployment of efficient robotic systems for these extreme conditions are critical challenges.
6️⃣ Strategic Importance 🛰: The development of a lunar propellant production capability is viewed as a strategic move that could secure economic leadership in space for the U.S. and other participating nations. It would also fuel broader space exploration efforts, potentially supporting human settlement on the Moon and Mars.
7️⃣ Government and Legal Roles ⚖: Governments are expected to play a significant role in supporting this commercial endeavour, not only through technology development and prospecting missions but also by addressing gaps in international law, particularly around property rights in space.
Space technology is evolving incredibly fast, but many of the observations made in this paper are still highly relevant.
Note: Image from the original paper.
Feasibility of harvesting lunar ice to create a new source of space propellant (short read)