Navigating the Immersive Technology Frontier: Realities, Challenges, and Future Possibilities.
According to some, immersive technologies are expected to revolutionise the way we interact with the world around us. According to others, they are somewhat overhyped and full of challenges. In this article, we explore the potential of immersive technologies, talk about challenges and the most likely way forward. We will touch on a range of topics, including the promise of AI-enhanced virtual worlds and the challenges in hardware, software, and user experience, as well as some of the profound questions about privacy, accessibility, and the very nature of human-computer interaction.
Defining Immersive Technologies
Immersive technologies can be broadly categorised as follows:
- Virtual Reality (VR): Fully immersive digital environments that replace the real world.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Digital overlays that enhance the real world with virtual elements.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Blending real and virtual worlds where physical and digital objects coexist and interact.
- Extended Reality (XR): An umbrella term encompassing VR, AR, and MR.

Maturity assessment
Immersive technologies are rapidly evolving but have yet to reach full maturity. Considering the current trajectory of technological advancements and adoption rates, we can anticipate that this frontier will mature in the medium to long term, approximately within the next 5 to 10 years. During this period, we expect to see significant improvements in accessibility, affordability, and integration with other technologies, leading to broader adoption across various sectors and profound impacts on society and the economy.

Applications Across Industries
Expert views vary on which sectors will be most impacted by the advancements in immersive technologies. The consensus is that gaming and entertainment will benefit far more than other industries, but significant benefits are also expected in healthcare, marketing and advertising, education and training, and retail and commerce.

Example applications include:
- Gaming and Entertainment: Immersive gaming experiences, virtual concerts, and interactive storytelling.
- Healthcare: Virtual therapy sessions, patient rehabilitation, and medical imaging visualisation.
- Education and Training: Virtual classrooms, simulation training for medical procedures, and skill development.
- Retail and E-commerce: Virtual try-ons, immersive product demonstrations, and interactive shopping experiences.
- Manufacturing and Design: Virtual prototyping, collaborative design environments, and maintenance simulations.
Market Size and Growth Projections
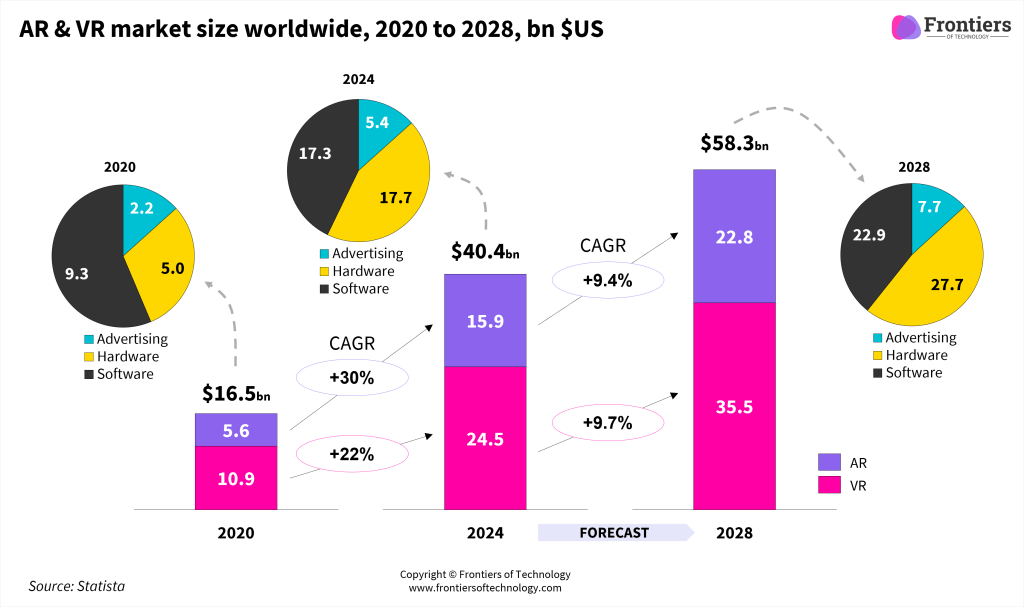
The global Immersive Technologies market revenue has grown at a compound annual growth rate of 25% over the last 4 years, reaching around $40bn in 2024, including VR revenue of $24.5bn and AR revenue of $15.9bn. It is forecast to increase further by c.9.6% CAGR over the next 4 years, reaching $58bn in 2028.
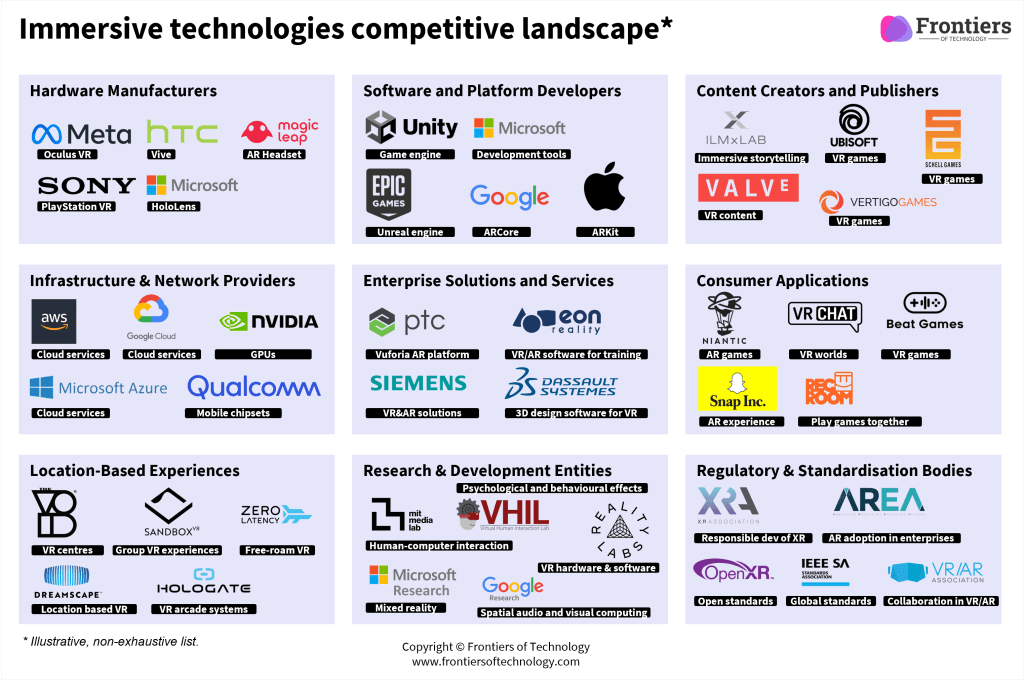
Key Market Players
Below is a list of some of the most prominent organisations across multiple categories in the immersive technologies landscape:
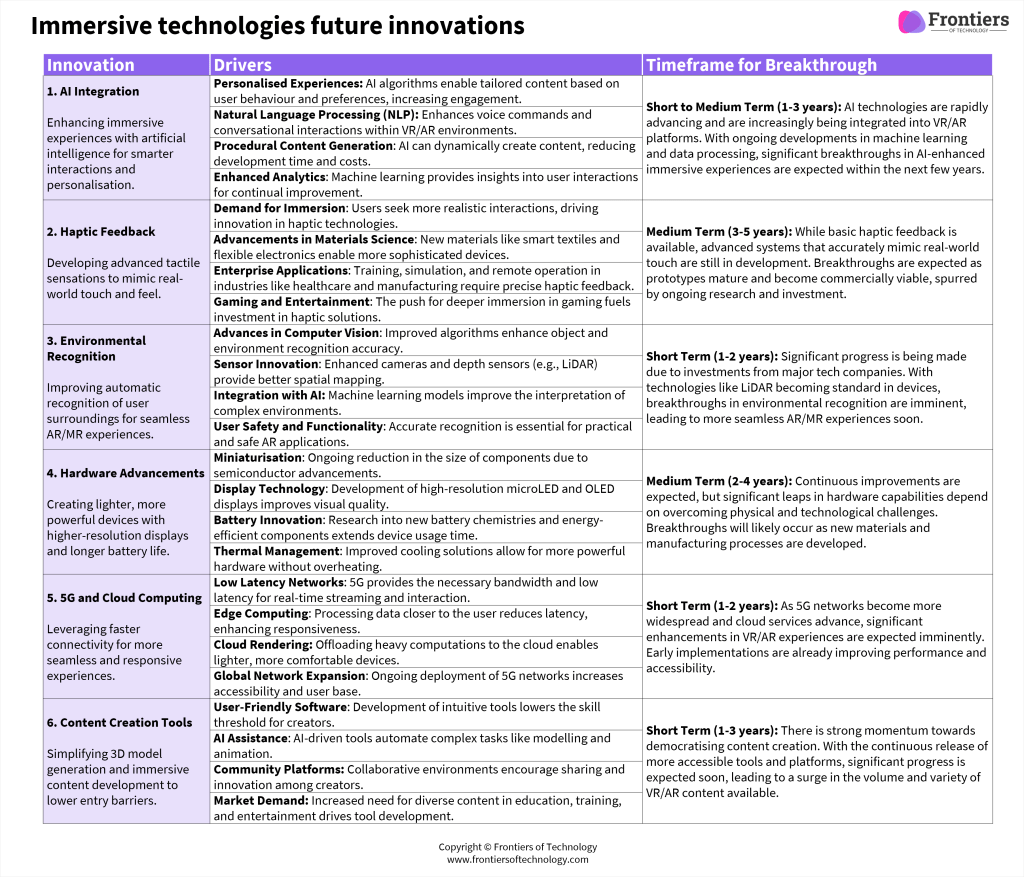
Technological Innovations
We believe there are 6 key areas of technological innovation that will contribute to future breakthroughs in this frontier:
- AI Integration: Enhancing immersive experiences with artificial intelligence for smarter interactions and personalisation.
- Haptic Feedback: Developing advanced tactile sensations to mimic real-world touch and feel.
- Environmental Recognition: Improving automatic recognition of user surroundings for seamless AR/MR experiences.
- Hardware Advancements: Creating lighter, more powerful devices with higher-resolution displays and longer battery life.
- 5G and Cloud Computing: Leveraging faster connectivity for more seamless and responsive experiences.
- Content Creation Tools: Simplifying 3D model generation and immersive content development to lower entry barriers.
A range of challenges are currently blocking a more rapid expansion of immersive technologies, including:
- Accessibility and User-Friendliness: Making immersive technologies more user-friendly and affordable for mass adoption.
- Interoperability Across Platforms: Ensuring compatibility and seamless experiences across different devices and platforms.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: Addressing data privacy issues as devices become more capable of scanning and understanding surroundings.
It will also be interesting to see how the frontier will address some of the key trade-offs, which will then determine which solutions are likely to be more successful and which businesses are likely to take a higher market share:

It’s also interesting that depending on how these trade-offs play out and what innovations happen at what time, we could see very different immersive technology futures manifesting over the next 5-10 years:
Device Form Factors:
- Lightweight AR Glasses: Vision of all-day wearable devices seamlessly integrating digital and real worlds.
- Advanced VR Headsets: Focus on immersive experiences with powerful, but less portable, hardware.
Impact on Daily Life
- Transformative Potential: Immersive environments could change how we shop, consume media, and socialise.
- Niche Applications: Alternatively, the technology may remain specialised for certain industries or entertainment forms.
Overall, what’s fascinating about this frontier, is the scale at which industry experts disagree on the speed of developments in this space. According to some, immersive technologies will render traditional TVs and smartphones obsolete by 2030. According to others, widespread adoption of AR/VR devices is decades away due to technological and social barriers. We strongly believe that this will depend on the speed at which the industry will solve the innovation challenges outlined above.
We track the most impactful research breakthroughs and innovations across all key frontiers. Stay connected with us for regular updates and insights.

